⚡Quick Answer
- Choose the Editor: Start by selecting your preferred editor – Gutenberg Block Editor, Classic Editor, or a page builder like Divi or others.
- Access the Editor: Log into your WordPress dashboard, navigate to the page or post you want to edit, and open it in the chosen editor.
- Make Edits: Use the editor’s features to add or modify text, images, and other elements on your page or post.
- Preview and Publish: Always preview your changes to ensure they look right before publishing them to your site.
For detailed step-by-step instructions, please read on.
What You Need to Edit a WordPress Site
Before we start with this guide, make sure you have the following:
- The WordPress website admin URL (Example: yourwebsite.com/wp-admin/)
- Login credentials of the admin area
- Gutenberg (or WordPress Classic Editor) installed and available
- Page builder if you want to edit codeless on front-end
Once you have all these, open the admin URL and log in to your WordPress dashboard.
How to log into WordPress:
- Go to your WordPress login page (usually at yourwebsite.com/wp-admin/)
- Use your username or email address and password to log in
- Sometimes you can also log in directly from your WordPress hosting dashboard without using login credentials
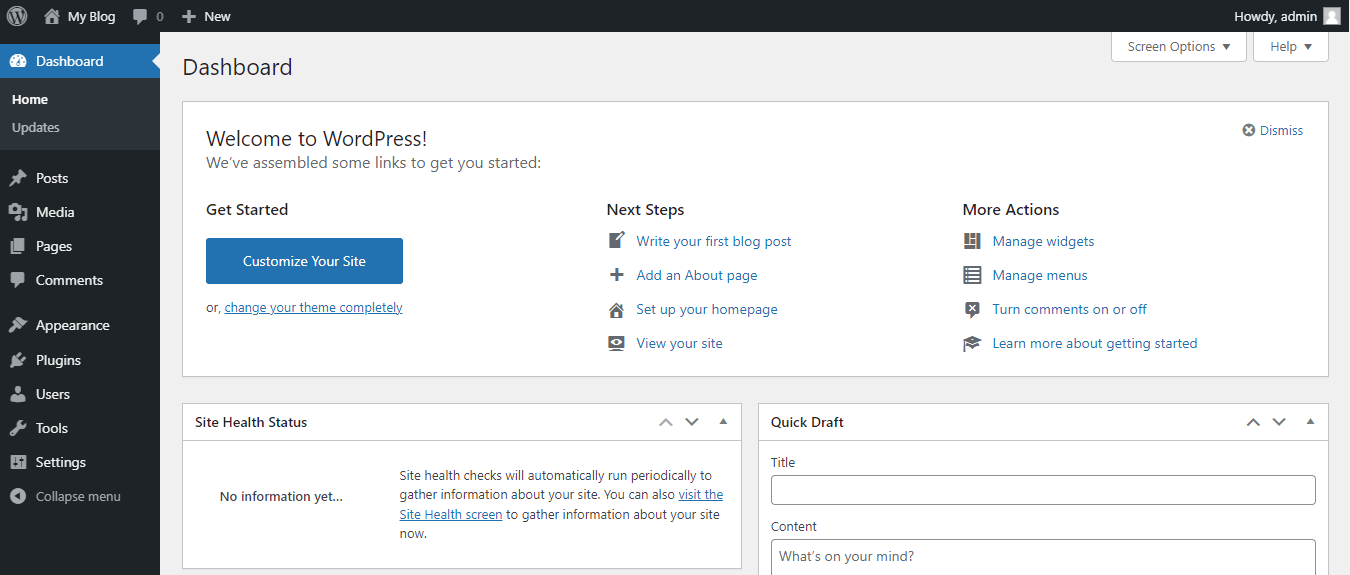
Once successfully logged in, you land in your WordPress dashboard.
WordPress dashboard is the place where WordPress editing happens if you are not using a front-end page builder.
Once you have successfully logged in to your Dashboard, you can start editing your WordPress website.
⚠️ Make sure you backup your site with a reliable backup plugin like UpdraftPlus. Wrong edits can cause unexpected issues, and it’s always a good idea to have a backup ready to restore if anything goes wrong.
WordPress Editing Basics
In this section, we’ll discuss the basic WordPress elements that you will most likely deal with when editing your WordPress website.
These elements are:
- Posts & Pages
- Theme
- Editor
📄 Posts & Pages
There are two forms of content on WordPress:
- Posts
- Pages
WordPress posts are for dynamic and time-sensitive content. These are usually blog articles. However, if you want you can use WordPress posts for other time-sensitive content too, like events.
The posts are displayed in reverse-chronological order – the newest ones are displayed first. Posts usually have RSS feed and comment section connected to them.
In contrast, WordPress pages are for static content.
Homepage, contact us, about us, privacy policy, and other types of static pages are usually uploaded as WordPress pages.
So, when you edit WordPress, you edit one of these two things – posts or pages.
You can also make edits in the WordPress dashboard, but those edits are usually of technical nature.
⚡ Check also: How to Edit Footer in WordPress
🎨 Theme
WordPress theme is a framework that controls the overall design of a WP website and in some cases adds additional functionality to the website.
This additional functionality may vary from none to impressively rich toolsets.
In a standard case, WordPress comes with default WP themes pre-installed.
These themes are usually given years instead of names, such as “Twenty-Twenty-One”:

✏️ Editor
The current default WordPress editor is called Gutenberg (also known as WordPress Block Editor).
Gutenberg was introduced in 2018 with WordPress 5.0 version. It replaced the previous WordPress editor which is now called a “classic” WP editor (aka TinyMCE).
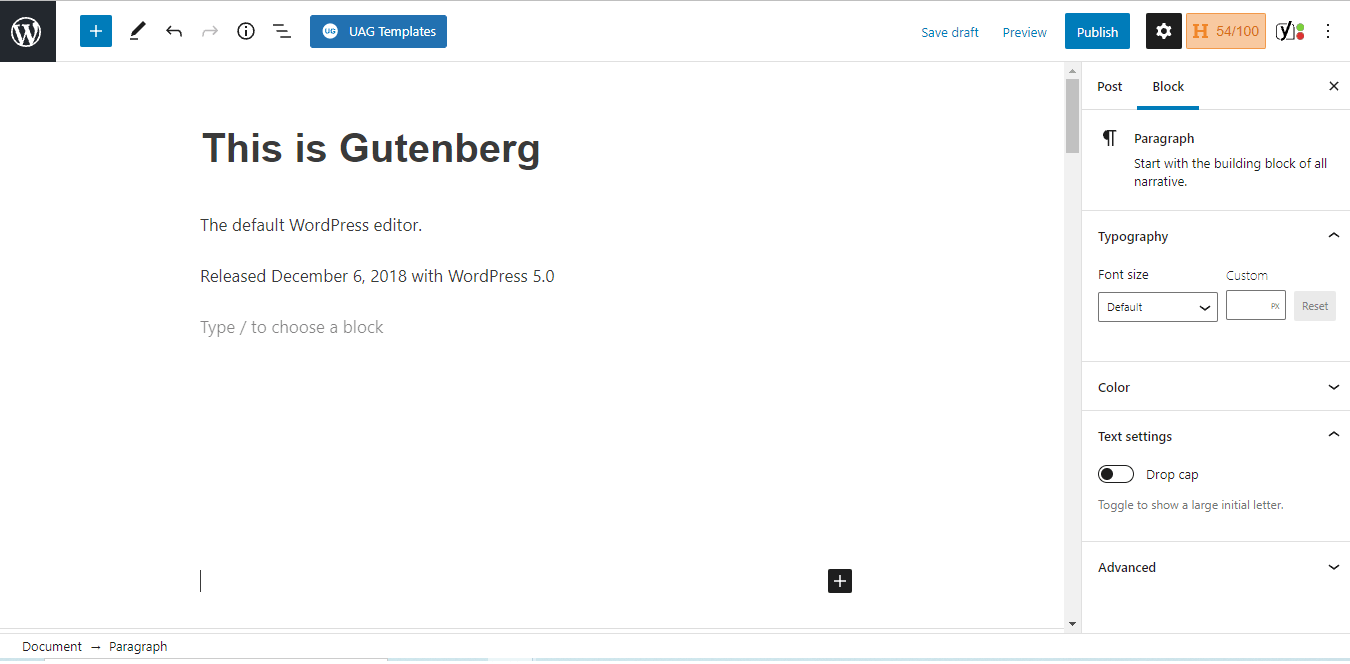
Generally, Gutenberg is quite intuitive. It’s based on blocks and every block is a piece of content.
Currently, there are the following Gutenberg blocks available:
| General Blocks | Formatting Blocks | Layout Blocks | Widget Blocks |
| Paragraph | Table | Separator | Archives |
| Heading | Code | Spacer | Calendar |
| List | Custom HTML | Page Break | Categories |
| Quote | Preformatted | Buttons | Custom HTML |
| Image | Verse | Columns | Latest comments |
| Gallery | Pullquote | More | Latest posts |
| Audio | Classic | Media and Text | Search |
| Video | Group | Shortcode | |
| File | Reusable block | Social icons | |
| Cover | Row | Tag cloud | |
| Stack | RSS | ||
| Page list |
This is how some of these blocks work:
- Paragraph block
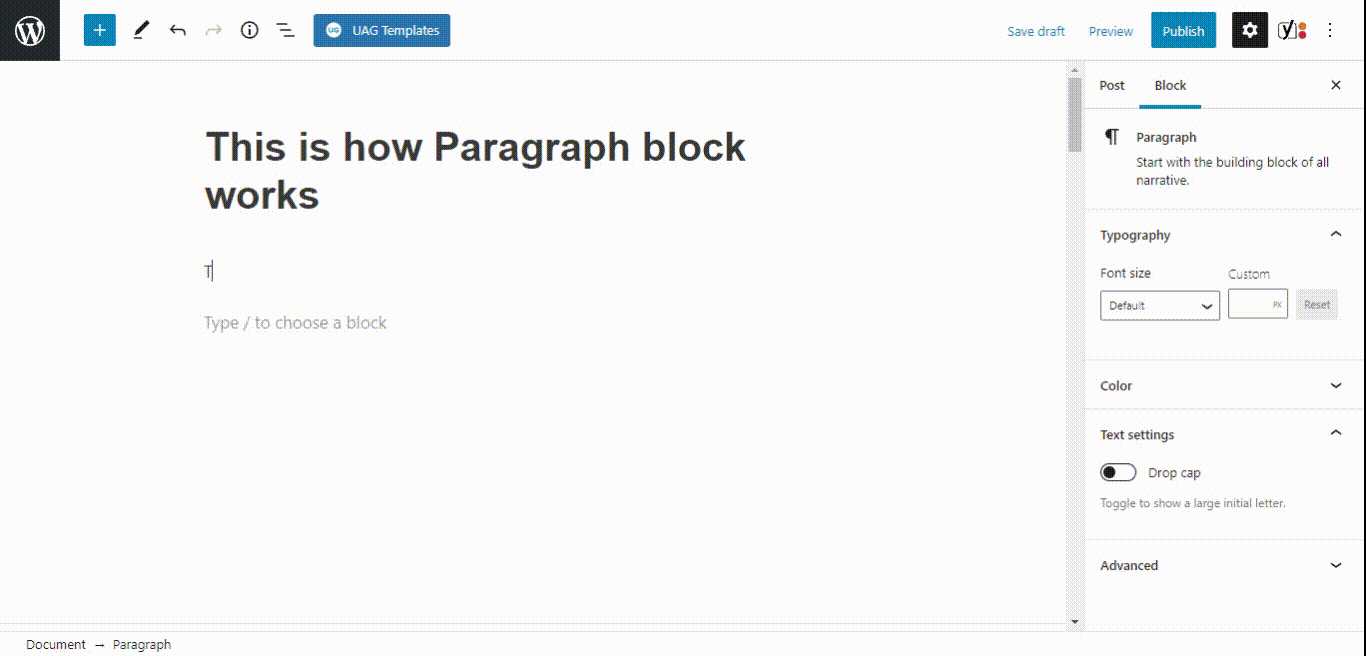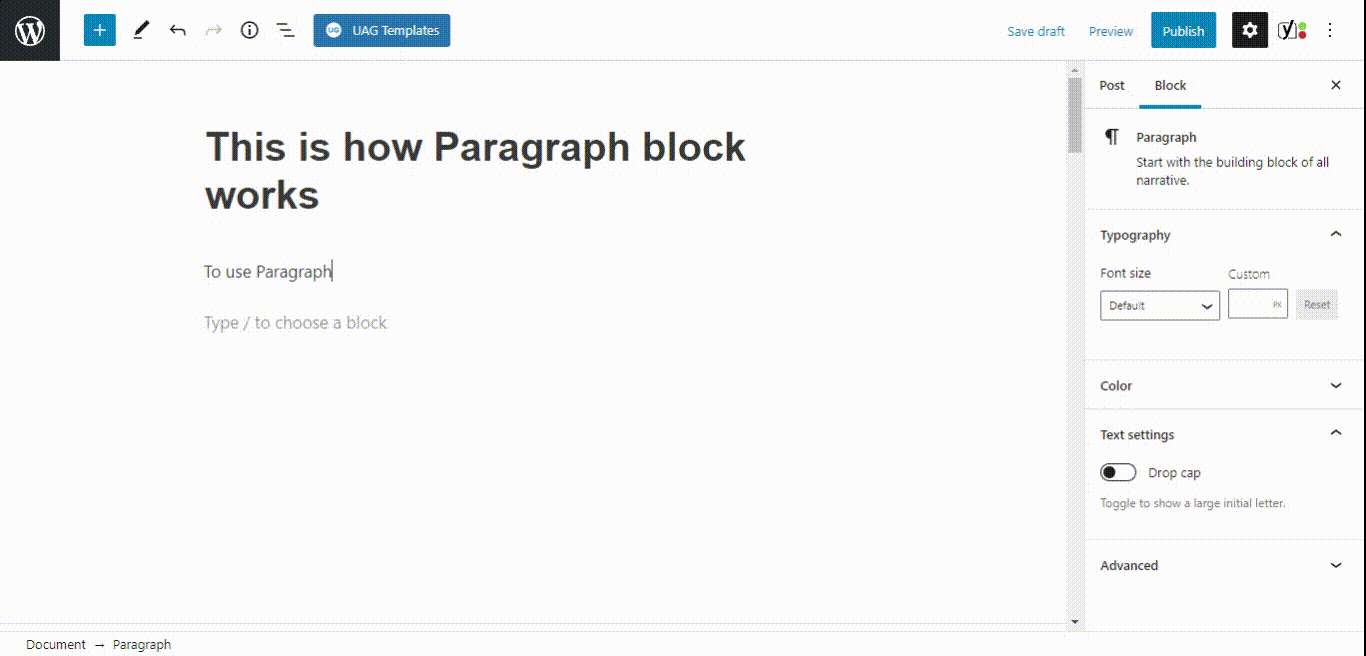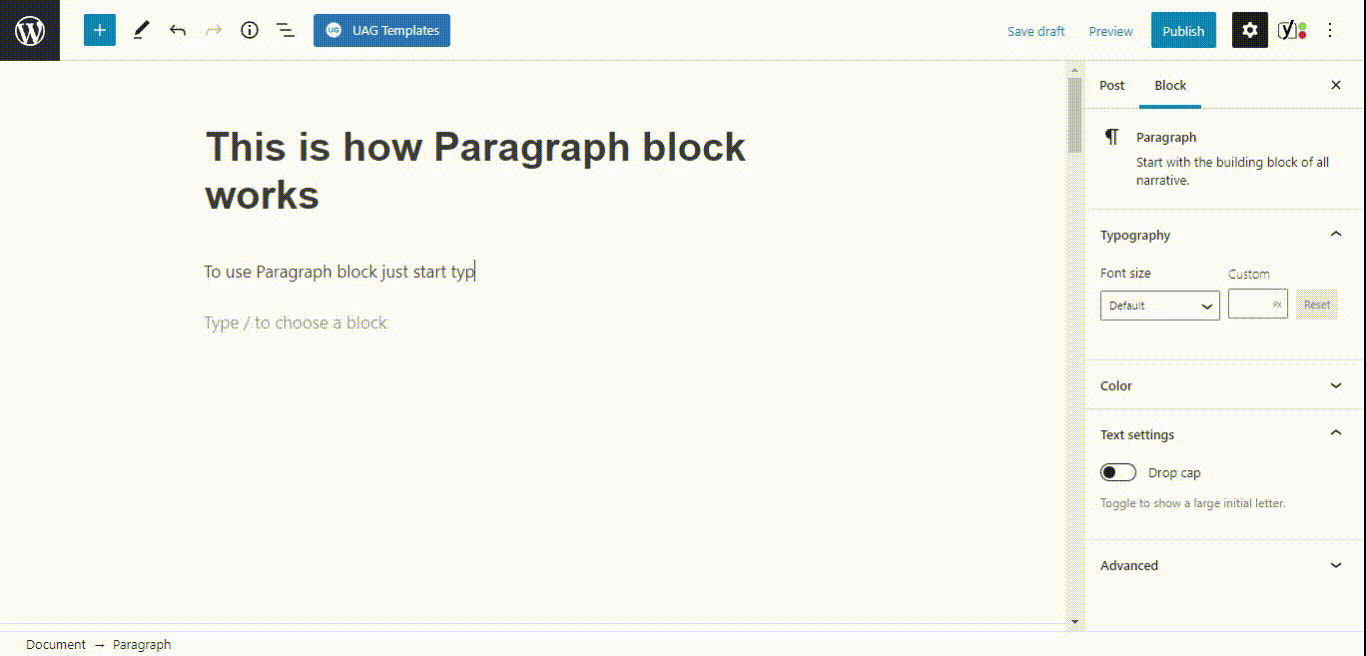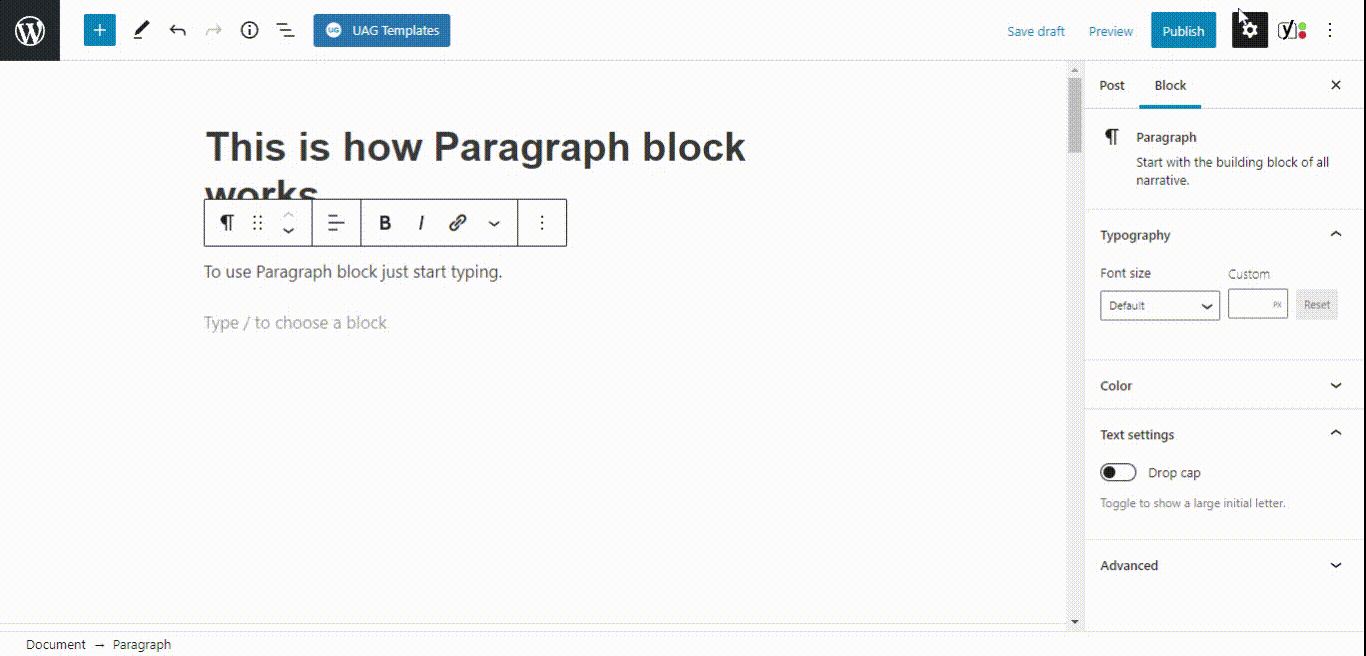
- Buttons block
So, yes, everything is extremely user-friendly and highly intuitive.
How to edit pages in WordPress
➡️ Go to the main article: How to Edit a Page in WordPress
Creating new pages and editing existing ones in WordPress is extremely easy.
How To Create Pages on WordPress
To create and start editing a new page on WordPress:
1. Go to pages (or posts, if you want to create a new post) in your WordPress Dashboard. You can also simply hover over it and options will show as below:
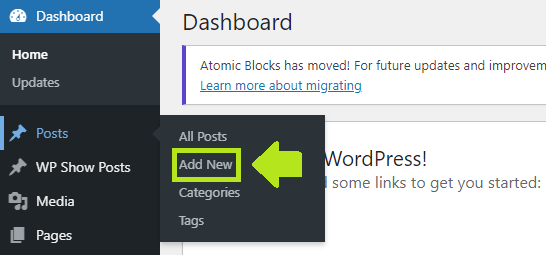
2. Click “Add New”
3. Gutenberg editor will load
4. Here you can start adding new content
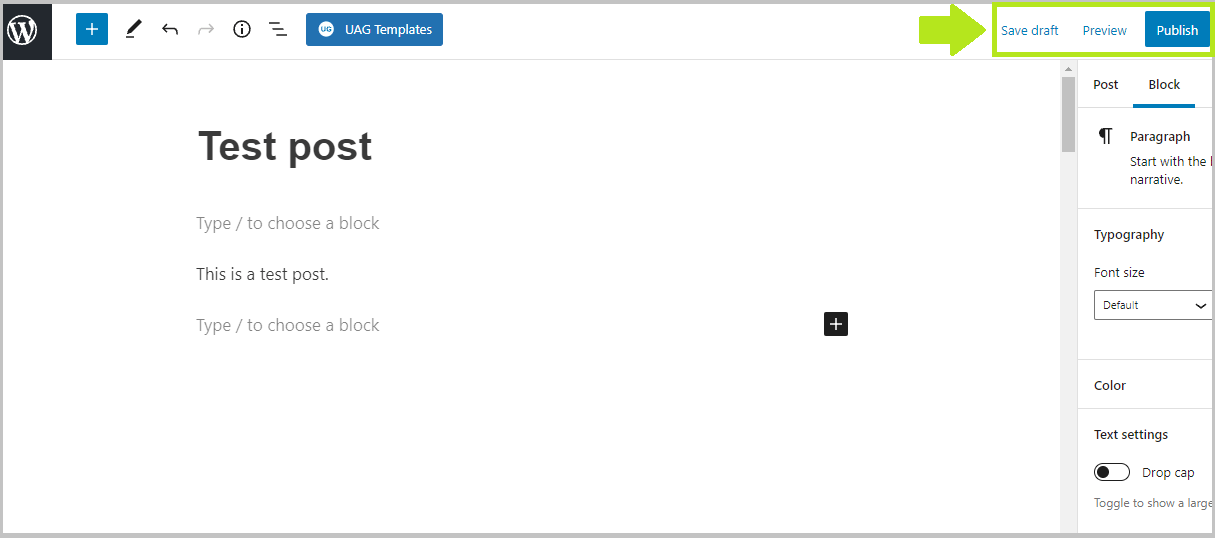
5. Once you are done editing you can either save the page/post as a draft or publish it:
How To Edit Existing Content on WordPress
To edit existing content on your WordPress website:
1. Go to posts/pages in your WordPress Dashboard
2. Click on the name of the post or hover over and click “Edit”
3. Gutenberg editor will load
4. Click on anything you want to edit and look for the options that pop up:
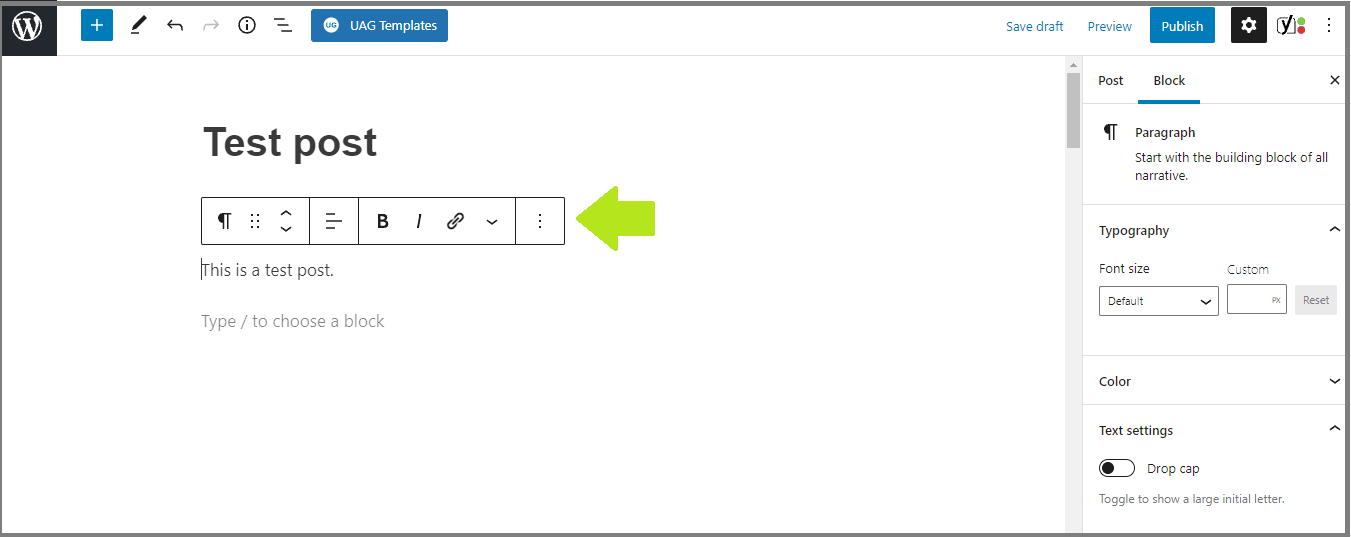
5. If you want to add a new element (block) click the plus icon (or type /) and choose what you want to add:
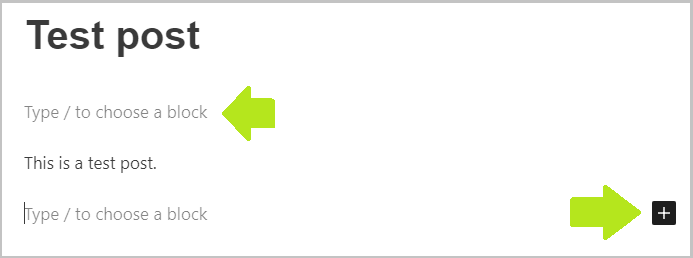
6. Most of the blocks have further customization options in the right sidebar:
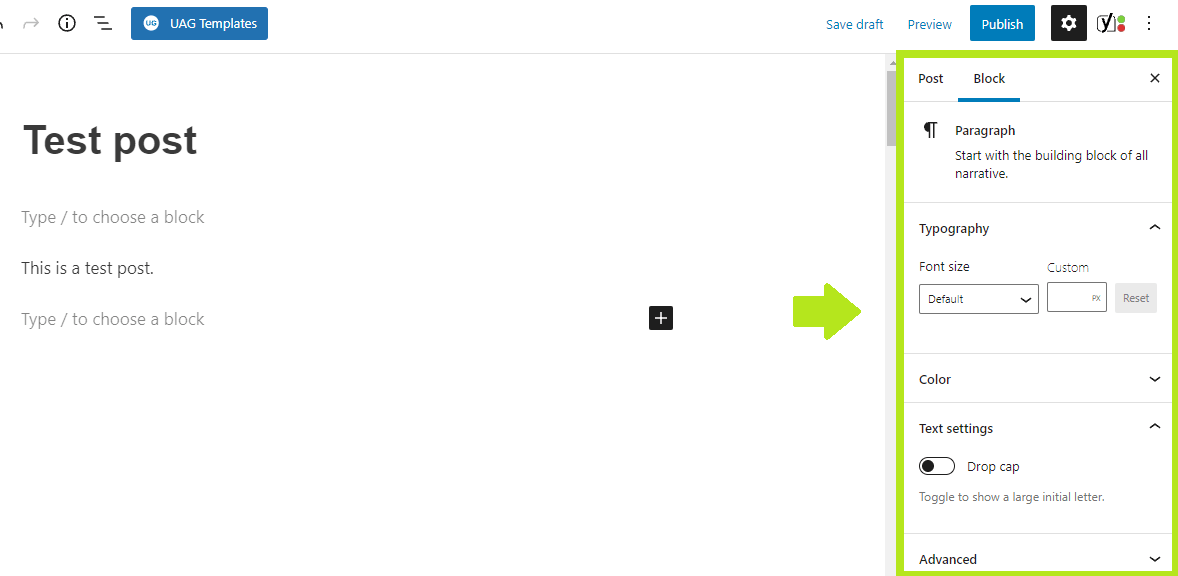
7. Customize things until you get the final output you want
This was the basic overview of editing on WordPress. Now let’s get into the details.
How to Edit WordPress Site Using the Block Editor (Gutenberg)
To edit any post or page in the WordPress site using the new Gutenberg Block Editor, navigate to Posts/Pages > Add New in the WordPress dashboard.

You can also open any existing post/page from Posts/Pages to edit.
Now on the page editing screen, you can start adding (or editing) content.
First, click on the Add title block and enter the page title you want. For existing content, you can edit the title the same exact way – by clicking on it.
Next, click enter (takes you to the first line after the title) and start typing to add the content you want.
As mentioned in the previous sections, each element in the Gutenberg is called a block (that’s why the name is “Block Editor”). If you want to edit or customize a block, you can click on it and select the settings from the sidebar.
Additional customization settings (for example typography settings like font size, drop cap, and font color for paragraph block) are available by default for all blocks.
To add an image to the page, click on the plus icon, and select the Image block from the popup.
You can also add other content elements by clicking on the plus icon and using the left sidebar’s search field.
Once you’re happy with the page content, click on the Publish button, and your page will get live instantly.
Note: You can click on the Preview option (in the top bar) to check how the page will look to the site visitors on mobile, tablet, and desktop.
How to Edit WordPress Site Using the Old Classic Editor
This Classic WordPress editor is powered by TinyMCE JavaScript software, which enables the customization options of the editor.
TinyMCE is a web-based editor and an open-source platform built with HTML and JavaScript.
🔔 Note
After the introduction of Gutenberg, if you want to use the Classic editor you need to enable it as a plugin.
Alternatively, you can use the Gutenberg block called Classic. It’s the same classic TinyMCE editor but in the form of a block.
Now to use the editor, you can go to your WordPress dashboard, and add a new post or page.
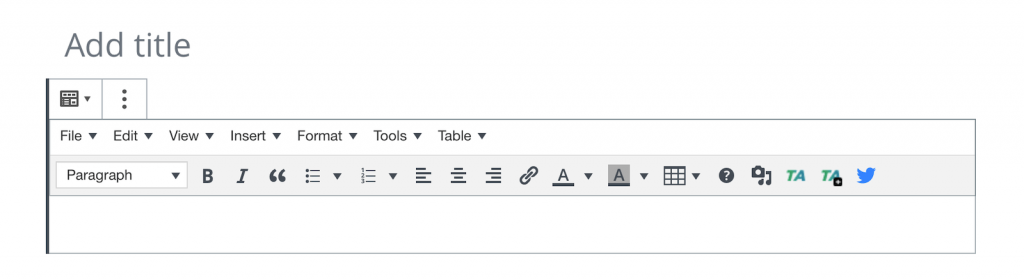
The WordPress editor is the main focus of the page from where you can control almost all the aspects of how your final published page will look like.
A few things you can customize with the Classic editor:
- Heading tags — H1, H2, H3, and so on…
- Font styles — bold, italics, and strikethrough
- Lists — bulleted and numbered
- Alignment of the elements
- Text and background colors
- Tables
- and Media — images, videos, etc.
The classic editor also supports custom styles so you can customize almost anything including the design and behavior of the page and its elements.
The classic WordPress editor is designed to keep everything simple and for basic things only. In contrast, Gutenberg and third-party WordPress editors such as Divi or Elementor take the WordPress page building experience to a whole new level and you can use these to create almost any type of layout you want.
Plus, with advanced WordPress page builder plugins, you can build right on the page (this is called the front end) in real-time instead of building on the WordPress dashboard (back end) and constantly switching between editor and preview.
How to Edit WordPress Site with Page Builders
The new Gutenberg Block Editor that comes with newer versions of WordPress is great for blog posts and basic page layouts. But it’s not designed to build advanced and more complex pages like a professional-looking homepage or sophisticated landing pages out of the box.
So for that, you can take advantage of a page builder.
WordPress page builders give you the power to create posts and pages without any coding knowledge, exactly how you want them.
Most page builders offer front-end editing that lets you build pages in real-time using the drag and drop content elements.
They are called WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) builders.
WYSIWYG mode makes editing WordPress blogs and pages a breeze!
The two most popular WYSIWYG WordPress page builders are Elementor, Divi and Beaver Builder.
Let’s now see how you use these page builders to edit your WordPress website…
How To Edit a WordPress Website With Elementor
Elementor is an insanely popular WordPress page builder with over 5M+ users. You can use Elementor to create pages, edit themes, and build full websites with beautiful design — all without touching a single line of code.
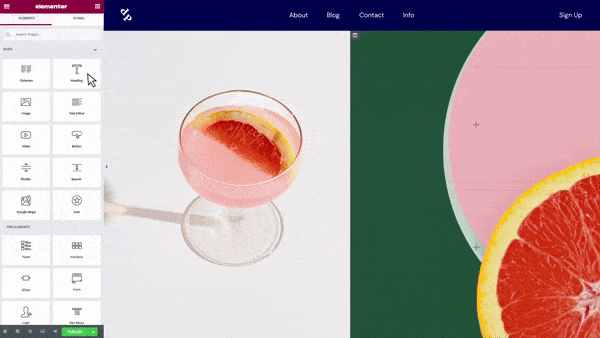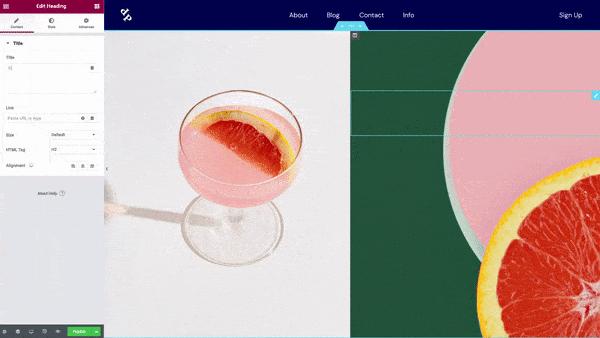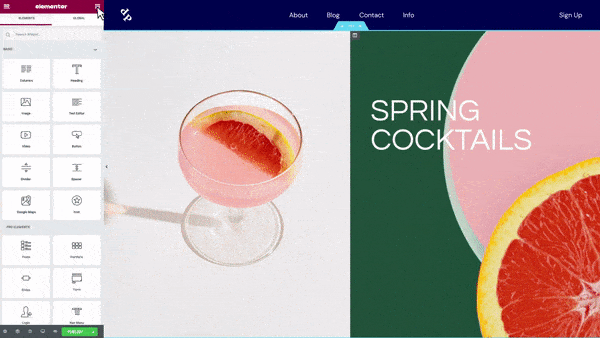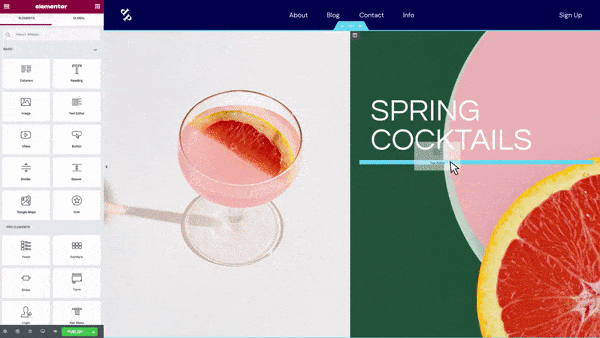
To start editing with Elementor, go to Plugins > Add New in your WordPress dashboard, and search for Elementor in the search bar.
Then click Install Now, and Activate.
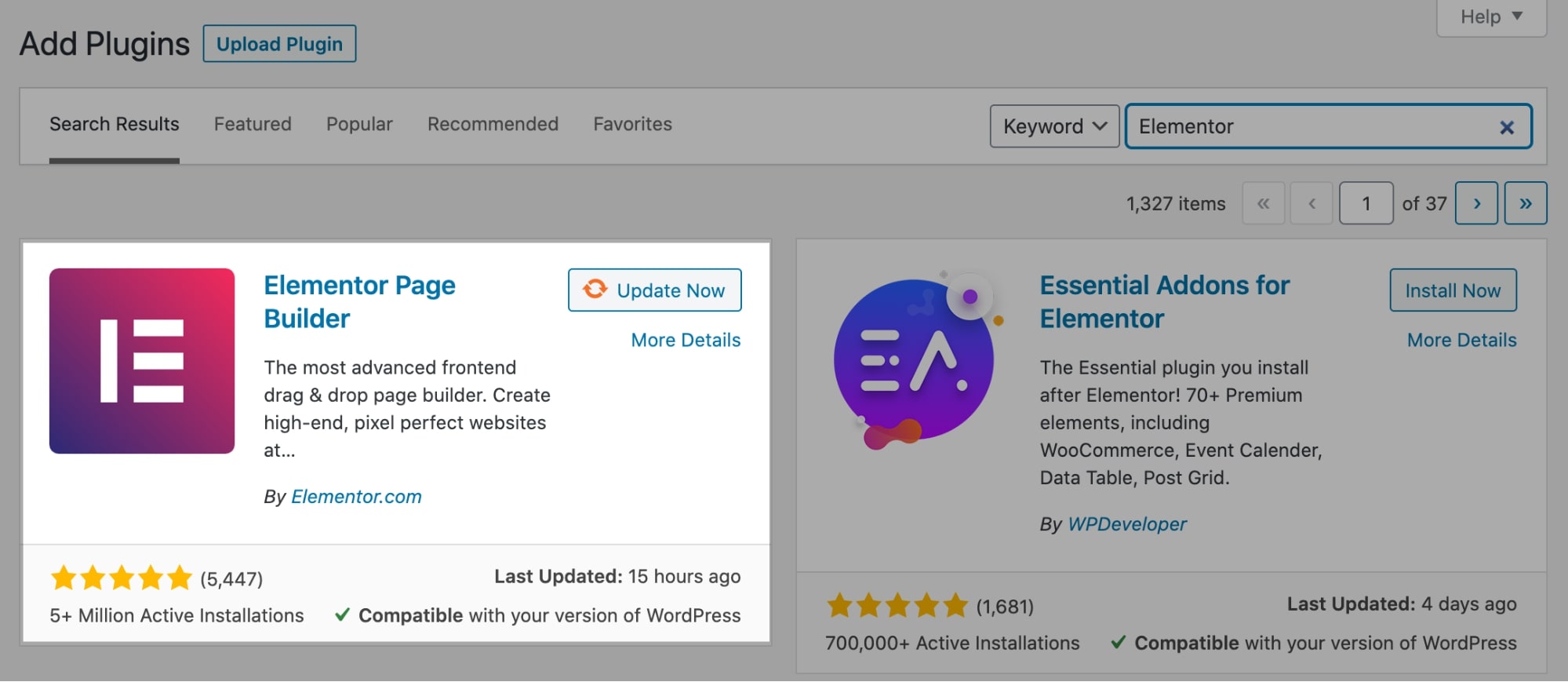
You can also get Elementor for free here.
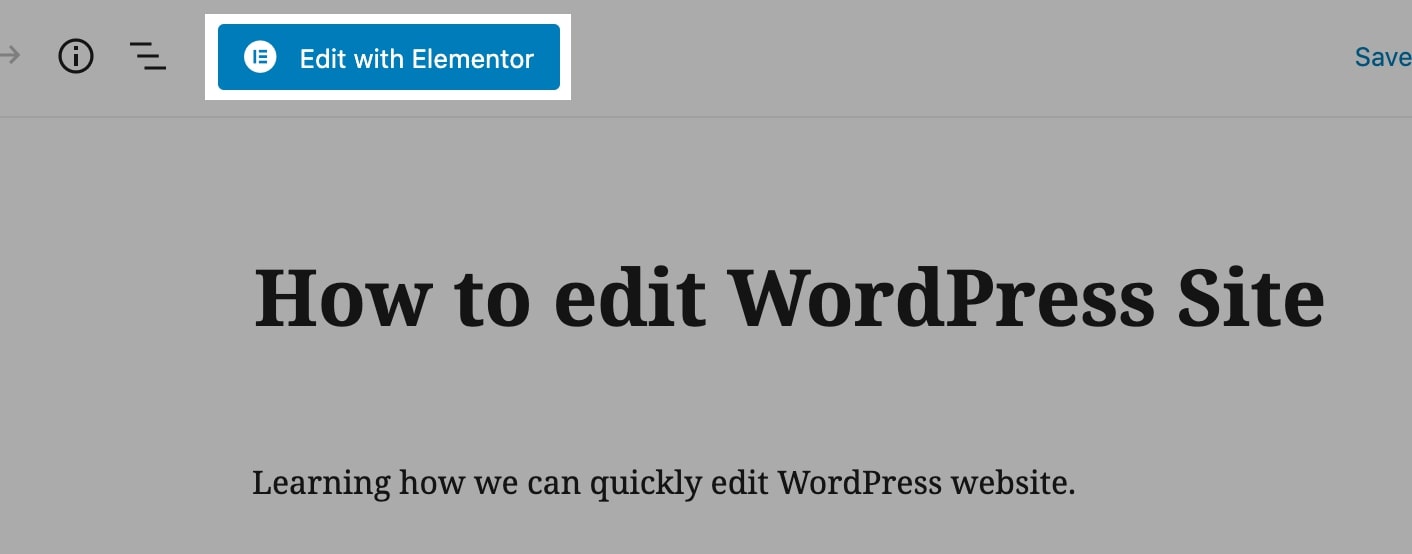
Then go to Pages and either add a new page or open an existing page.
Now click on Edit with Elementor to start editing the page in the page builder.
You can click the plus icon to add a row, and then simply drag and drop any content widget from the left sidebar into the right side.
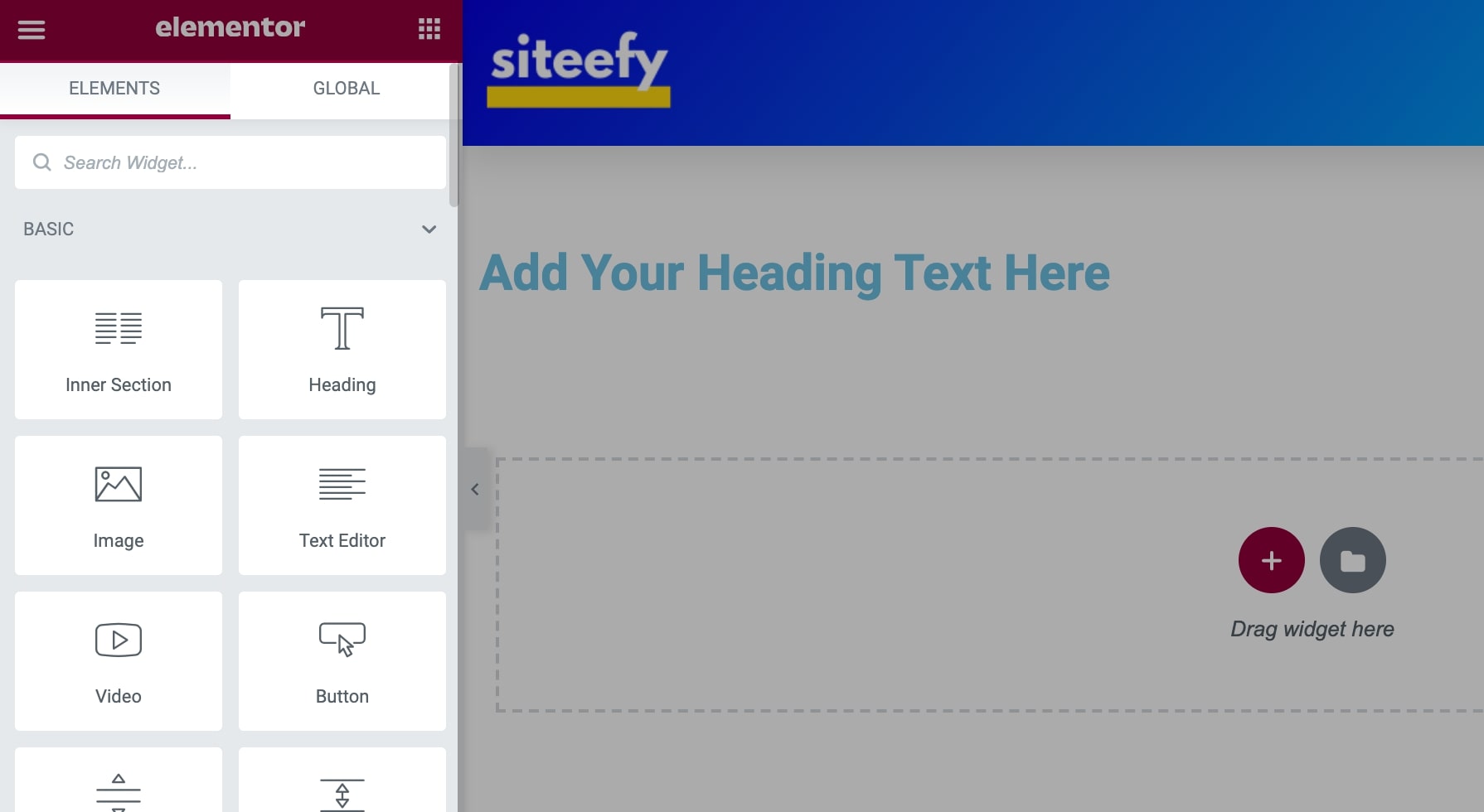
To modify or add any content, you can click on the text and start typing.
And to stylize it, you can select the different settings in the sidebar style tab.

You can add as many content widgets as you want to the page.
All widgets support multiple customization options like typography, margin/padding, colors, shadow, border, background color, and animations.
After you’re done editing the page, you can publish it or save it as a draft to publish later.
Watch this video to learn more about Elementor and what you can do with this powerful page builder…
How To Edit WordPress Websites With Divi Builder
Divi is another super popular WordPress builder with a community of over 700,000+ users. It’s a page builder with endless customization options, advanced features, and hundreds of beautiful pre-built layouts.

Unlike Elementor, Divi is a premium-only page builder. There is no free version of Divi Builder available. But Divi provides a free in-browser live demo which can be accessed here.
To edit your website with Divi Builder, go to the Elegant Themes website and download the Divi Theme file (which includes the Divi Builder as well).
Now in your WordPress dashboard, navigate to Plugins > Add New and click on Upload Plugin on the top. Select the downloaded Divi zip file and click on Install Now.
After that, you can go to any page and click the Use Divi Builder button to enter the editing screen.
In the next screen, you can either select the option to build the page from scratch or choose any pre-built template that comes for free with Divi Builder.
After that, you can click on the plus icon to add any row, column, or content element you want and start editing.
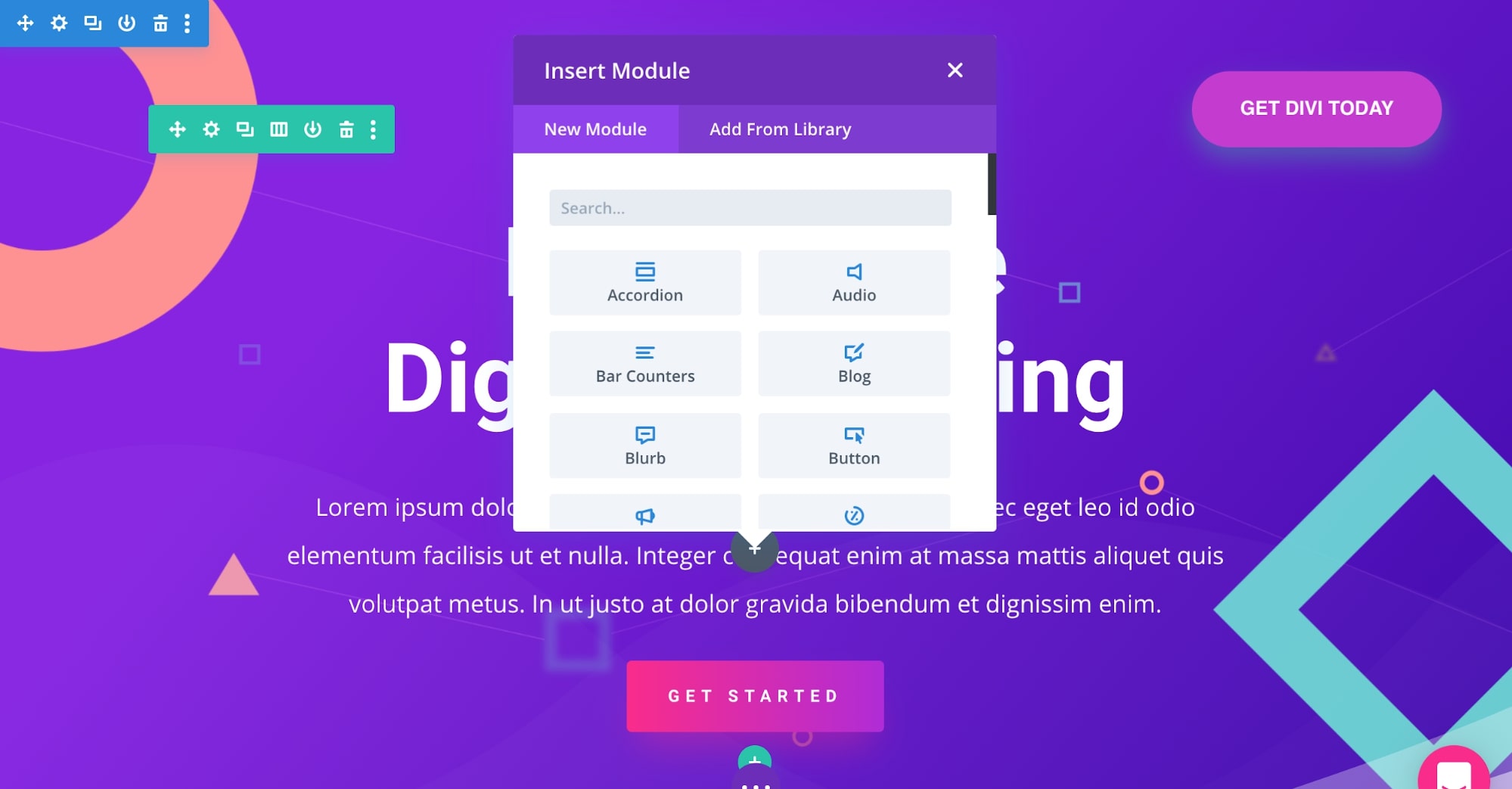
To edit the content of any widget, you can select it and then edit everything in the settings popup.
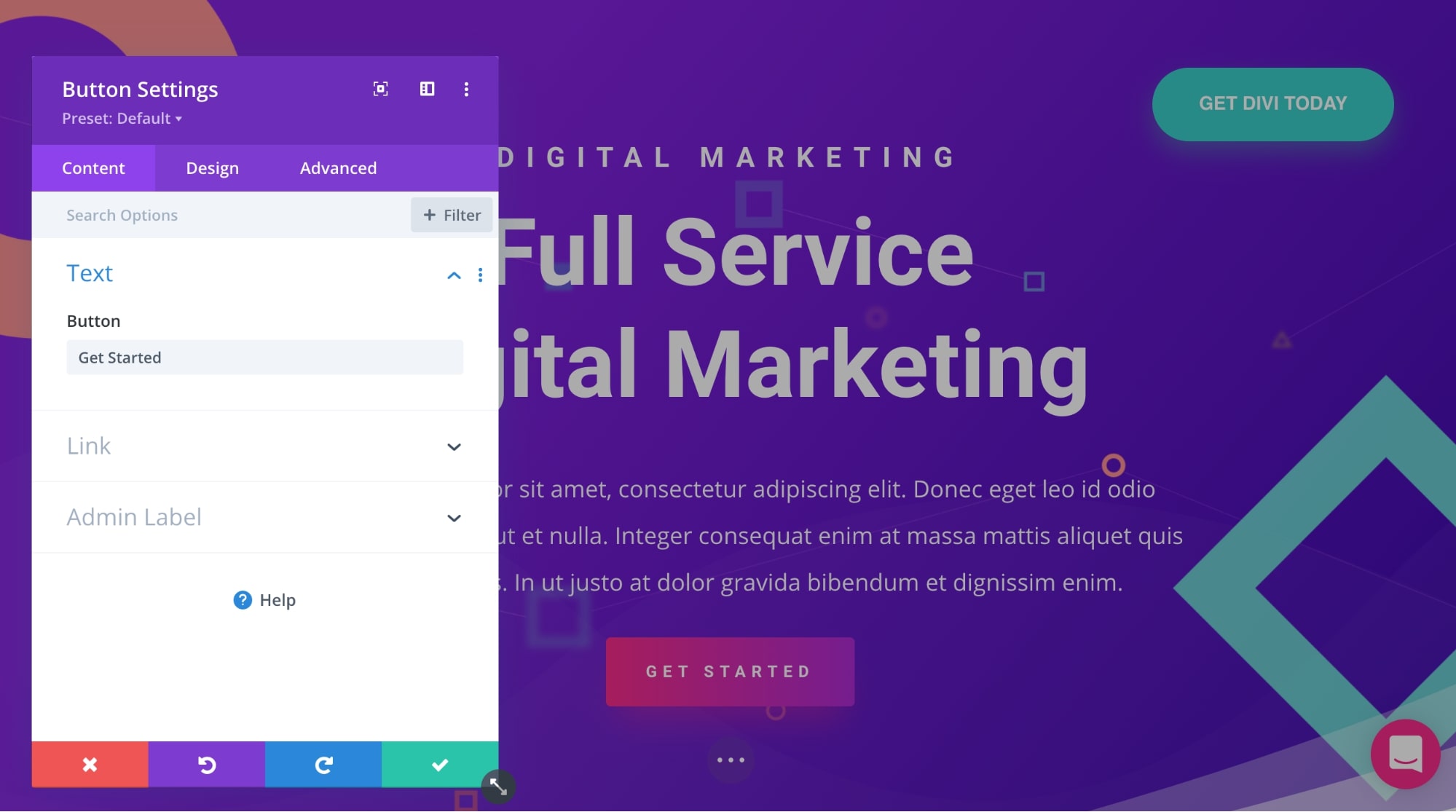
Divi includes multiple options for links, colors, spacing, shadow, filters, animation, and scroll effects.
Once you’re done with all the changes, you can click the Save button on the right.
Check this video to see how easily you can edit WordPress pages with Divi Builder…
How to edit WordPress Code
To edit code in your WordPress website, follow the below steps…
Edit WordPress HTML in Gutenberg (Block Editor)
In the Gutenberg editor, you can either add a dedicated HTML block where you can write all your HTML code within the page or edit the HTML of the full page (this can be slightly complicated if you’re not familiar with the basic syntax of HTML).
First, click on the plus icon and look for a custom HTML block. Then write all the HTML in the box, which will be applied to the page’s front end.
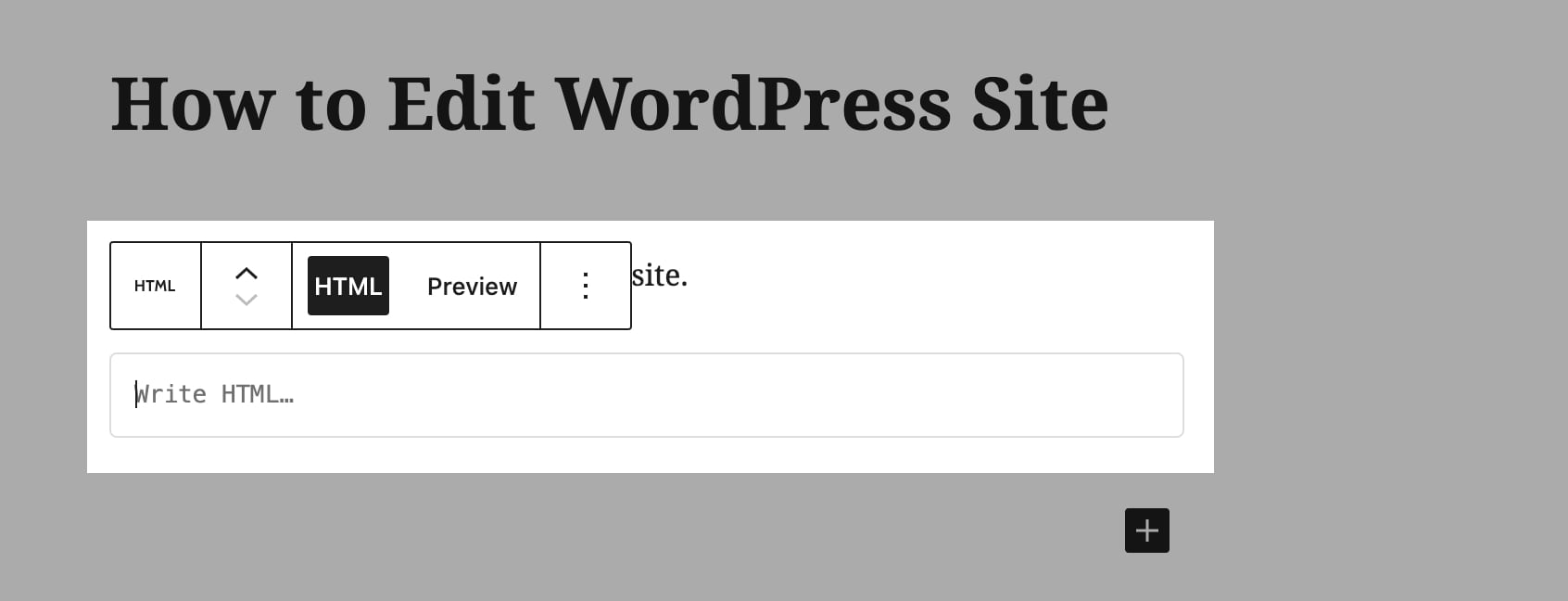
To edit the HTML of the entire page, click on the menu icon on the right sidebar and then select Code Editor.
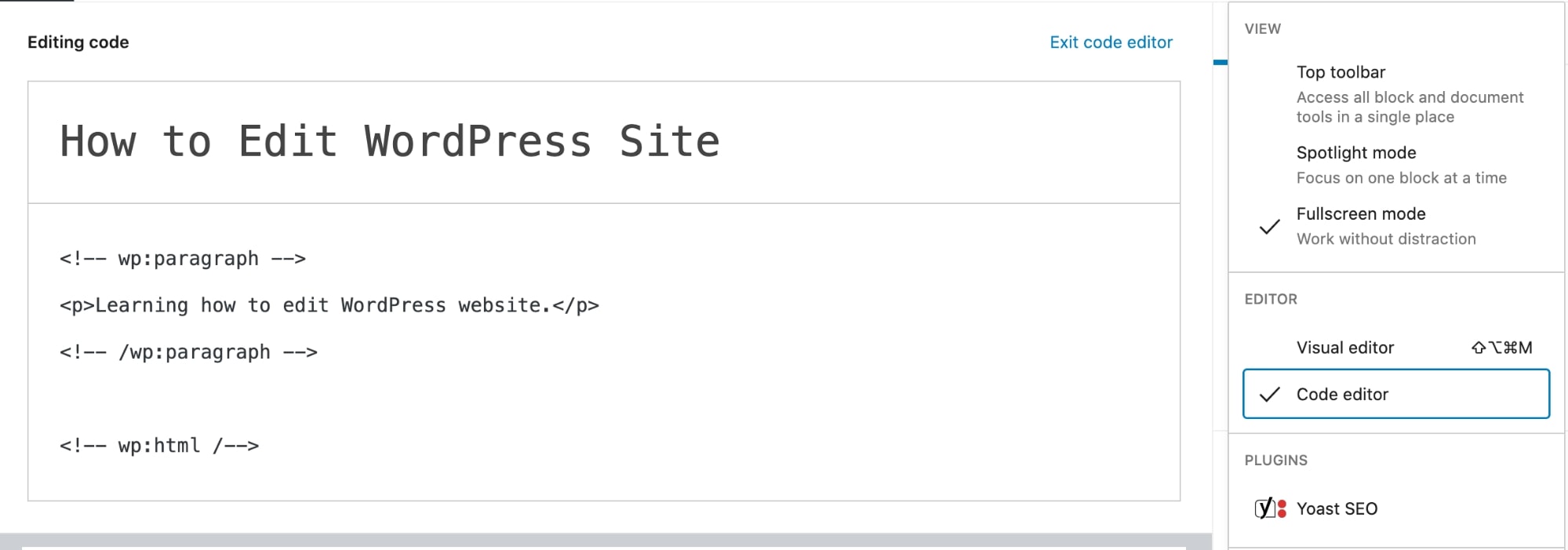
This is how to edit code in WordPress. Here you can write or modify all the HTML of the page.
Keep in mind that you will have to write everything with the proper markup for blocks in the code editor. Otherwise, the page will run into issues.
Edit Source Code using the WordPress HTML Editor
If you want to directly edit the theme code, you can access the Theme Editor and make all the modifications in the theme files.
To access the Theme Editor, go to Appearance > Theme Editor.
Here WordPress will give you the warning to make sure you don’t edit any critical theme files.
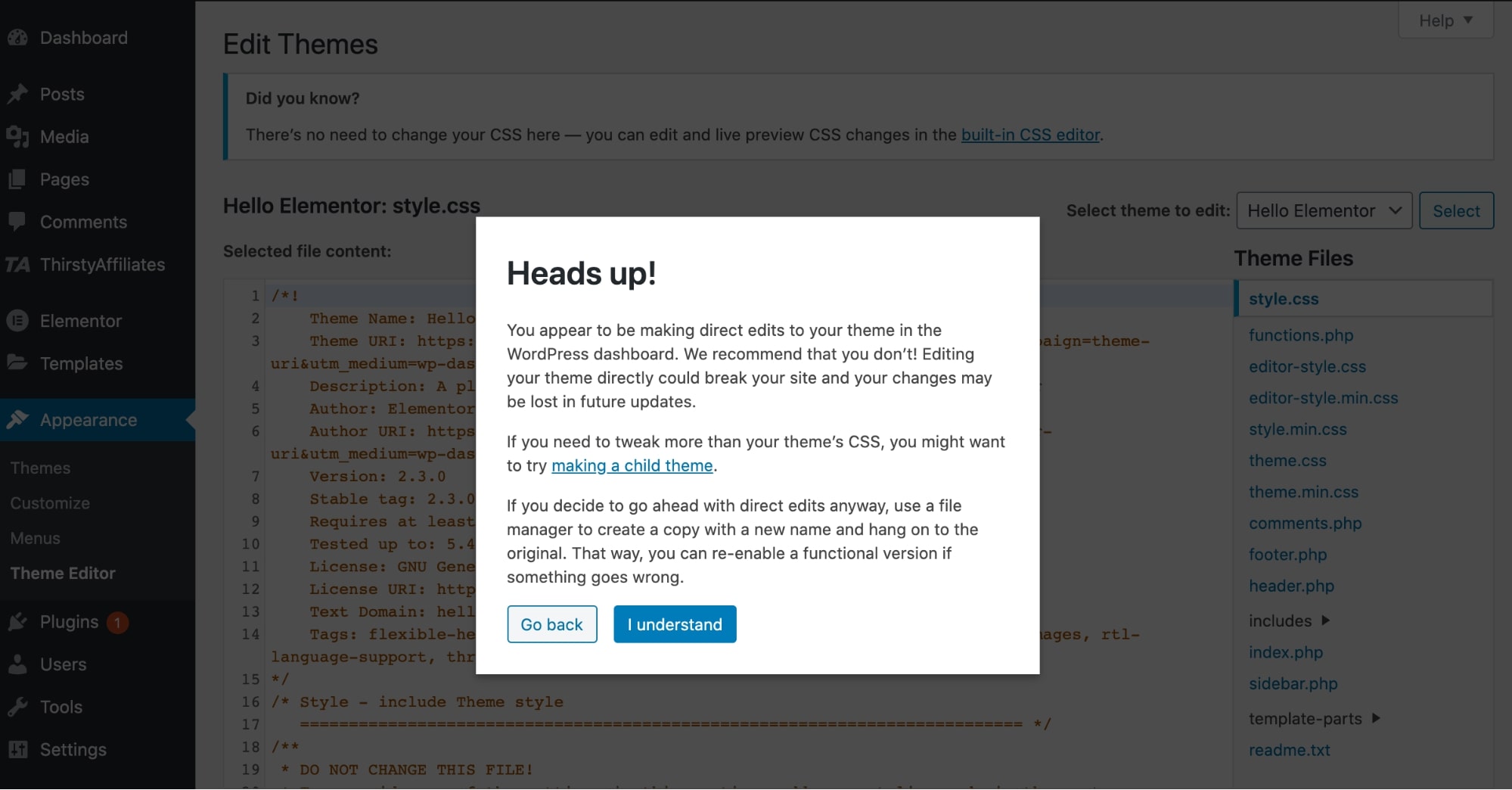
Simply click on I understand and then select the file you want to edit from the right side.
🔔 Note:
Take a full website backup before making any changes in the Theme Editor and editing code in WordPress. If you’re not sure how to edit the code, it’s better to hire a WordPress expert as any mistake here can easily break your WordPress site.
How to Edit WordPress Home Page
➡️ Go to the main article: How to Edit WordPress Home Page
The homepage is the front page of the website. It’s the first page that opens up when someone visits the website URL.
By default, all the blog posts are displayed in reverse chronological order on every WordPress site’s homepage.
But you can change this and set any custom page as the homepage to show the content you need.
How to set front page on WordPress:
- Go to Settings > Reading in the WordPress dashboard.
- Then click on “A static page” option and select the page that you want to set as your homepage from the drop-down list.
- Click on “Save Changes”, and you’re done!
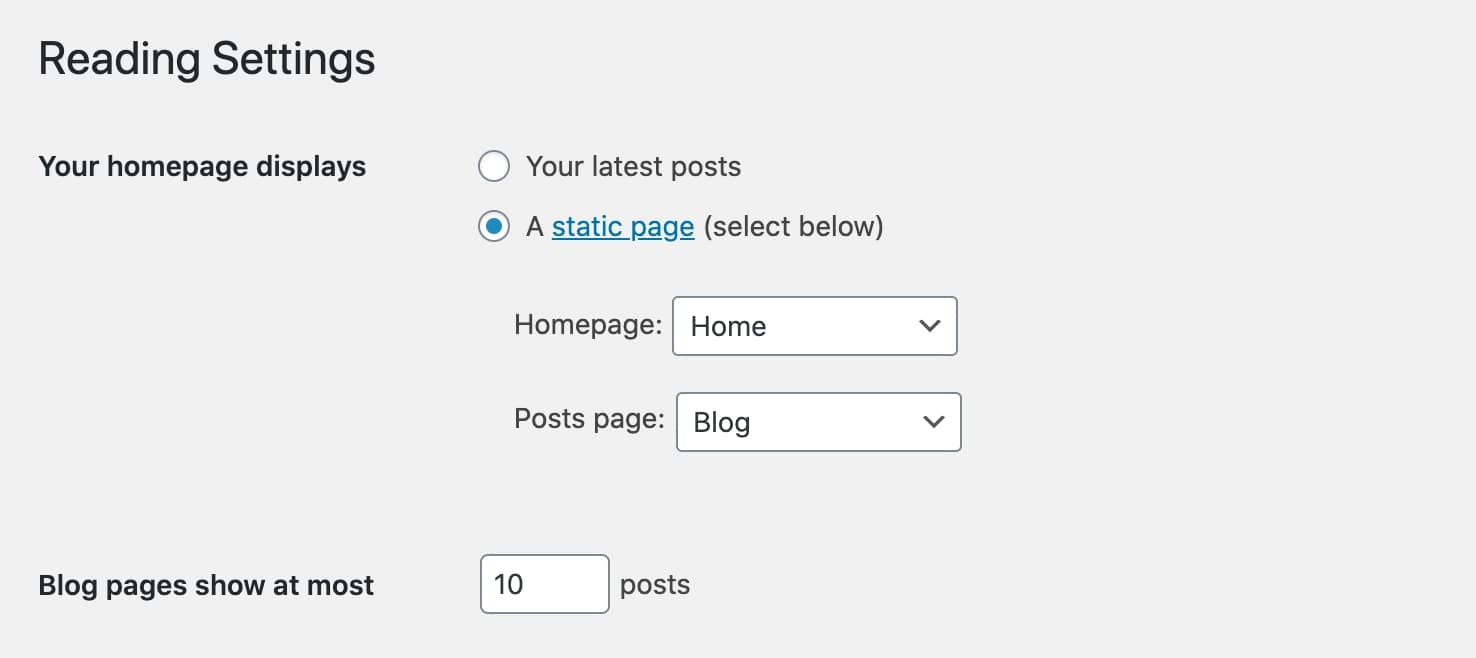
Now to edit the homepage, navigate to Appearance > Customize.
In the Customizer, you can click on the pencil icon to edit any element you want, and all WordPress home page edits will be in the live preview, in this case, so you can see how everything looks before publishing the page.
Once the homepage is final, click on Publish in the sidebar, and the new homepage will be live.
🔔 Important Note
The ability to edit the homepage in the WordPress theme customizer depends on the theme you’re using. Some premium themes like Divi offer endless customization options, while you won’t get many features in the free themes.
In other words, it’s hard to make your pages look exactly the way you want them with basic WordPress themes/editors and no coding skills.
To learn more about how to edit your homepage on WordPress check our article here. (Yes, we have a whole article on that 😎).
How To Edit Header in WordPress
Editing WordPress header will predominantly depend on what customization options your theme (or page builder) provides.
Premium themes usually provide a user-friendly way to make your heading look exactly the way you want it.
So, the first option would be to check if your current theme has an in-built way of editing the WordPress header.
For example, Divi theme provides a tool called Theme Builder which allows building tons of different things including custom-designed WordPress headers in a code-free manner:
Elementor offers a Theme Builder capable of customizing WordPress headers too:
So, using a theme builder is probably the most beginner-friendly (and user-friendly) way of editing WordPress header at the moment.
Without something like a theme builder (or alternative built-in functionality), you will most likely have to deal with code.
Other ways of making edits to WordPress header are:
- Using a standalone plugin (may require coding)
- Editing your theme’s header.php file in WordPress Theme Editor (requires coding)
⚡ Check also: How to Change the Link Color in WordPress
How To Edit Footer in WordPress
➡️ Go to the main article: How to Edit Footer in WordPress
Editing WordPress footer is a little easier than editing the header. This is mostly because the footer is a standard widgets place on WordPress websites and there are some easy-to-use built-in instruments to edit the footer in WordPress.
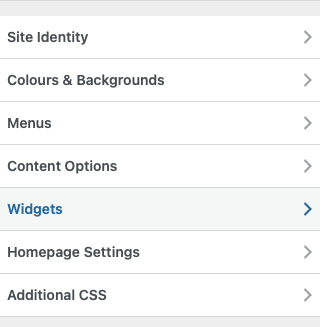
Here is how to customize WordPress footer:
- By going to Appearance > Customize > Widgets:
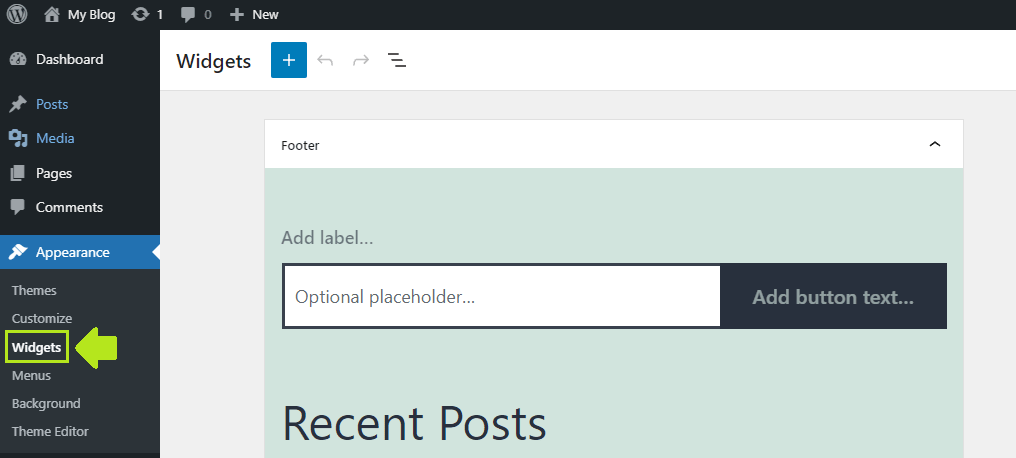
- By going directly to Widgets:
- Using Theme Builder (Divi, Elementor, Beaver Builder)
- Editing footer.php file (requires coding)
Check our article on editing WordPress footers for more information on this.
How To Edit Permalink in WordPress
Permalinks are simply the permanent URLs of your WordPress posts and pages.
Example: https://siteefy.com/how-to-edit-wordpress-site/
This is the permalink of this post.
Default WordPress permalink structure is based on the page/post name and date when the page/post was published.
But this can be easily altered.
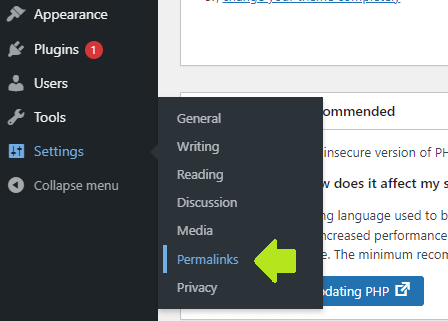
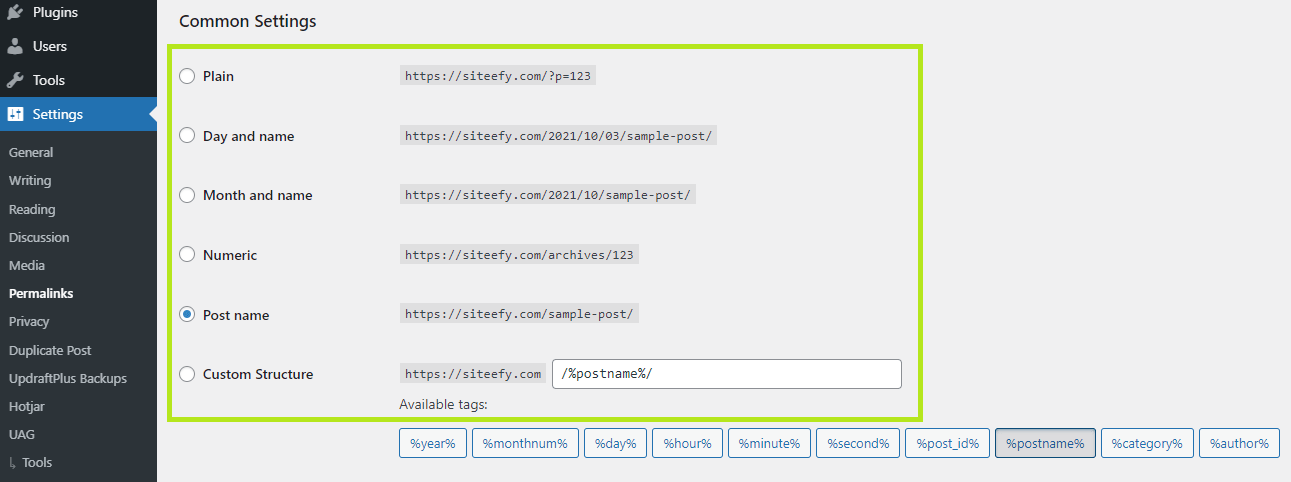
Here is how to change the default permalink structure on WordPress:
- Go to Setting > Permalinks:
- Choose the permalink structure you want and click Save Changes:
To change a permalink of an individual post/page look at the right sidebar options on Gutenberg:
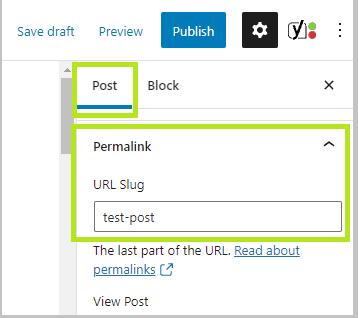
In WordPress Classic Editor, this option is right under the page/post title
How To Edit Menu in WordPress
Editing menu in WordPress is easy:
- Go to Appearance > Menus:
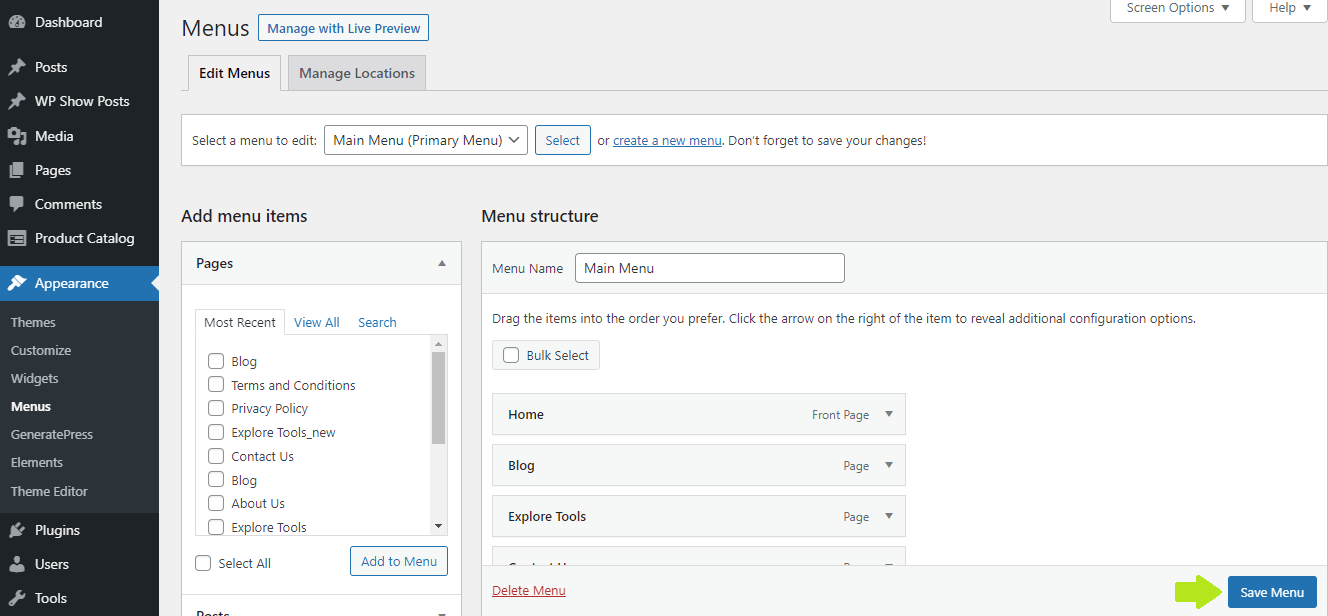
- Make all the changes you want and click Save Changes:
How To Change WordPress Site Title
You can change your WordPress site title in two places:
- Customizer
- Settings
Let’s look at each option.
How to change your WordPress site title in Customizer:
- Go to Appearance > Customize

- Next click Site Identity
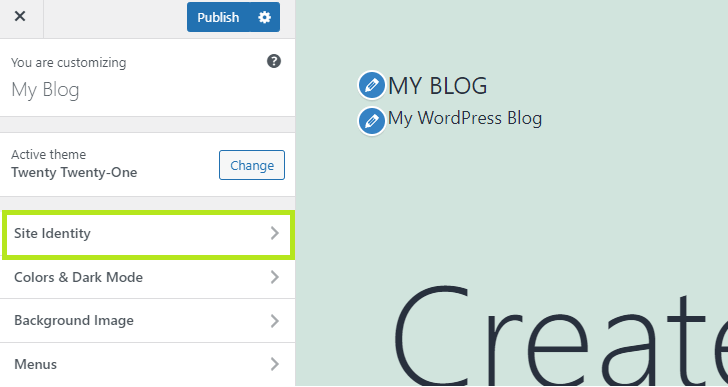
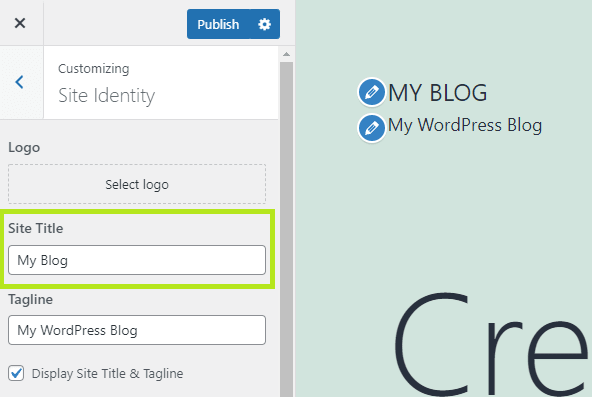
- Make your edits and click Publish
How to change your WordPress site title in Settings:
- Go to Settings > General
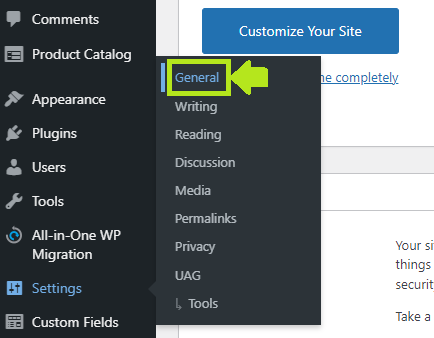
- Change your site title and click Save Changes.
How To Edit Mobile Version of a WordPress Site
➡️ Go to the main article: How To Edit the Mobile Version of Your WordPress Site
There are two beginner-friendly ways of editing the mobile version of your WordPress website:
- In WordPress Customizer
- With a page builder
Let’s look at both options.
How to edit the mobile version of your WordPress website with Customizer:
- Go to Appearance > Customize

- Look at the options at the bottom of the sidebar:
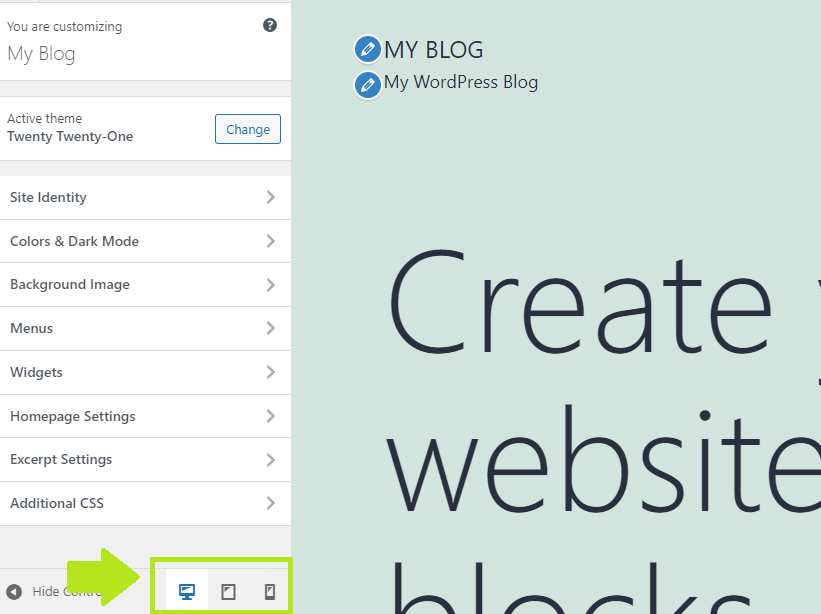
- Switch between Desktop, Tablet and and Smartphone options to see how your website looks on different devices and make edits.
How to edit the mobile version of your WordPress website with a page builder:
- Use Divi Responsive Editing:
- Elementor Responsive Editing:
- Most of other WordPress page builders also offer responsive editing.
Saving, Autosaving and Revisions on WordPress
When you’re editing a WordPress website, it’s important to know how your changes will be saved. WordPress has three different ways of saving your changes: autosaving, saving, and revisions.
Autosaving is the most basic way of saving your changes. WordPress will automatically save a copy of your changes every 60 seconds by default. This means that if you accidentally close your browser or lose your internet connection, you won’t lose all of your work.
Saving is a bit more manual, but it’s still pretty easy. To save your changes, simply click the “Save draft” button in the WordPress editor.

This will save your changes but won’t publish them to your website until you hit the “Publish” button.
Revisions are a bit more advanced, but they can be really handy if you need to go back and forth between different versions of your content. Automatic revisions are also enabled by default on WordPress.
To access your revisions, simply click the “Revisions” button in the WordPress editor.
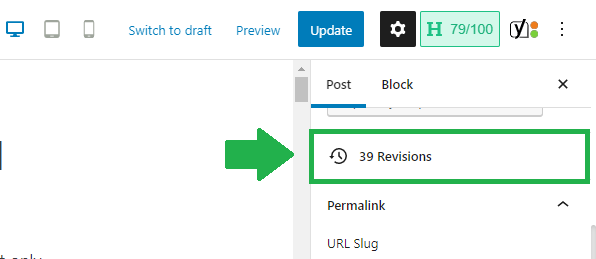
Keep in mind that autosaving and saving are two different things. Autosaving will save your changes automatically, but saving will only save your changes if you manually click the “Save draft” button.
If you’re not sure which method of saving is right for you, just remember that autosaving is the most basic way to save your changes. If you want more control over your changes, then saving and revisions might be a better option.
WordPress Shortcuts & Tips
| Shortcut | Windows | Mac |
|---|---|---|
| See the full list of all shortcut | Shift + Alt +H | Ctrl + Option + H |
| Save changes | Ctrl + S | Cmd + S |
| Copy a block | Ctrl + Shift +D | Cmd + Shift + D |
| Delete a block | Alt + Shift + Z | Ctrl + Option + Z |
| Insert a link | Ctrl + K | Cmd + K |
| Copy a block/text | Ctrl + C | Cmd + C |
| Paste a block/text | Ctrl + V | Cmd + V |
| Move down without line break | Shift + Enter | Shift + Enter |
| Switch to Code Editor (Gutenberg) | Ctrl + Shift + Alt + M | – |
⚡ Check also: How to Justify Text in WordPress
Other useful WordPress editing tips:
- To insert images you can simply drag and drop them from your PC to Gutenberg without using Media Library. Copy and paste works too.
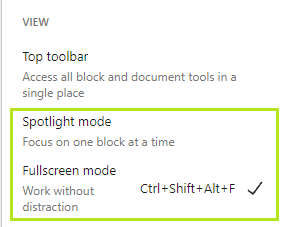
- To work distraction-free check Gutenberg’s Spotlight and Fullscreen modes (to see these options you need to click the three dots in the top right corner):
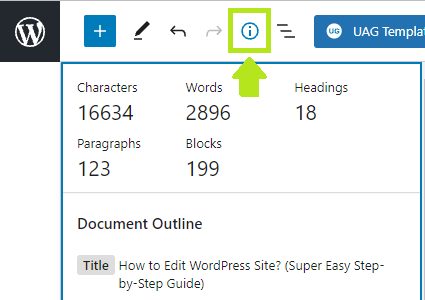
- Document outline function in Gutenberg is quite useful. It shows the number of words, characters, headings, paragraphs and blocks used in the article plus overall document outline.
- Copying from Google Docs to Gutenberg is a breeze – just copy and paste, and everything will look perfectly neat and clean.
WordPress Tools
As a WordPress user, you have access to a variety of tools and resources that can help you manage your site. These tools can be used to help you troubleshoot problems, customize your site, and extend your site’s functionality.
Here are some of the most popular WordPress tools and resources:
- The WordPress Codex: The WordPress codex is a comprehensive resource for all things WordPress.
- Jetpack – a plugin that provides a variety of features for WordPress sites, including security, performance, and site management tools.
- WooCommerce – a plugin that adds ecommerce functionality to WordPress sites.
- Yoast SEO – the most popular and widely used SEO plugin.
- Wordfence – Wordfence is a security plugin that helps to protect your WordPress site from malware and other security threats.
- UpdraftPlus – a backup plugin that helps you create, schedule and restore backups of your WordPress site.
- WPRocket – a caching plugin that helps to improve the performance of WordPress sites.
- Site Kit by Google – SiteKit is a free plugin by Google that helps you to connect your WordPress website to essential Google products such as Google Search Console and Google Analytics.
- Divi – Divi is a popular WordPress theme and page builder that turns your WordPress website into a drag and drop website builder.
- Monarch – Monarch is a social media sharing plugin that allows you to add social media buttons to your WordPress site.
- Bloom – Bloom is an advanced email opt-in plugin that allows you to grow your email list.
Editing WordPress – Summary
As we discussed in this post, you can use the new Gutenberg Block Editor to edit your WordPress website or try the powerful but very easy-to-use WordPress page builders. You can even edit the HTML of any page with Gutenberg blocks.
Overall, WordPress is a robust content management system with no particular restrictions on how you can edit the pages and the code, allowing for greater control over the website.
By following the steps listed above you should be able to start learning WordPress pretty fast and also be able to make all the initial edits you need to your new WordPress website.
If you have any questions related to this guide (or if you want us to extend it and cover more questions about editing WordPress sites), please let us know in the comments below.
FAQ
🔔 Check also:
- WordPress Tips: 17+ Ways to Improve Your Website and Workflow
- How to Justify Text in WordPress
- How to Change the Link Color in WordPress
- How to Add Blog Posts to Pages in WordPress
- WordPress: How to Remove “Leave a Reply”
- How to Make a Webcomic Site
- How to Edit Footer in WordPress
- How to Edit WordPress Home Page
- Why Is WordPress So Hard To Use?
- WordPress Visual Editor Not Working

Saksham, thank you very much. You have written this article beautifully step by step. And this article will be very effective for newcomers.
Hey Saksham,
Excellent share, so much helpful information on this post.
I love how to edit WordPress Code and Useful WordPress Shortcuts & Tips.
I’m going to put this into use sooner. Amazing work!
Hi Ricardo, I’m glad you liked this post. 🙂
Great! but what if the files are not available in child theme which I have to edit?
I’ve been blogging for 8 years on another platform. This is way too complicated for even a blogger with my experience.